고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
www.pyimagesearch.com/2020/07/06/region-proposal-object-detection-with-opencv-keras-and-tensorflow/
Region proposal object detection with OpenCV, Keras, and TensorFlow - PyImageSearch
In this tutorial, you will learn how to utilize region proposals for object detection using OpenCV, Keras, and TensorFlow.
www.pyimagesearch.com
Selective Search를 통해 제시된 regions를 활용해 분류를 어떻게 할 것인가?
파일구조:

라이브러리 임포팅
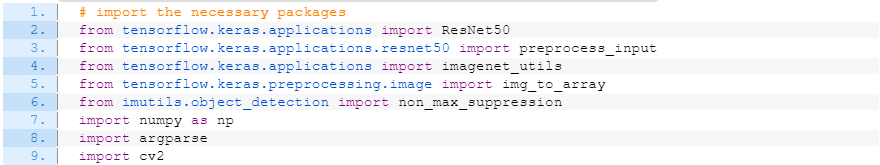
사용 도구: ResNet50, NMS (non_max_suppresion)
Selective Search를 함수화
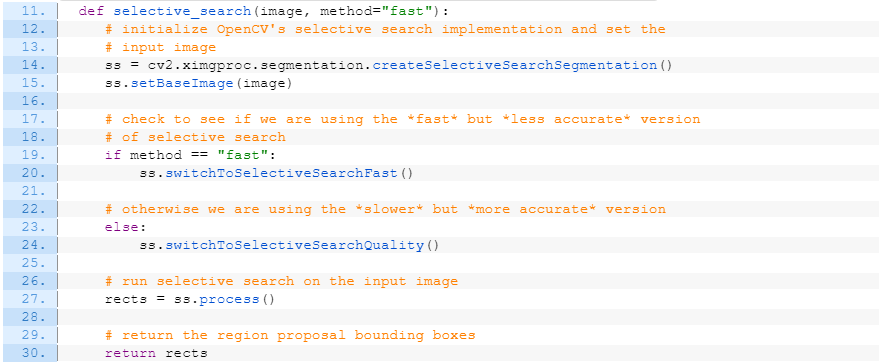
- 입력: 이미지 + 옵션 ("fast" 혹은 "quality")
- 출력: region proposals (rects)
bounding boxes에 대한 리스트 반환됨. 나중에 이 함수를 이용해서 입력을 bounding box로 받아 분류기를 통과시켜 ROI와 NMS를 적용할 예정 => 즉, object detector. (selective search가 임베딩된 end-to-end object detector 아님)
입력 정의:
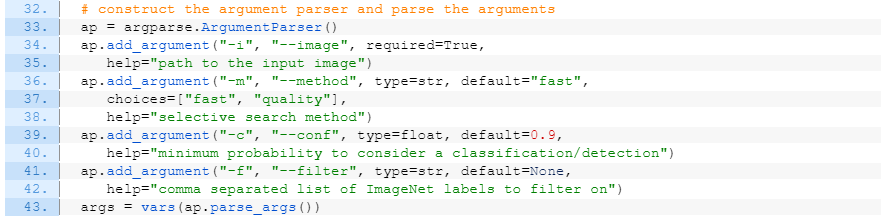
--filter 아규먼트를 좀 더 세밀하게 정의:

사전학습된 ResNet 초기화

Selective Search 적용
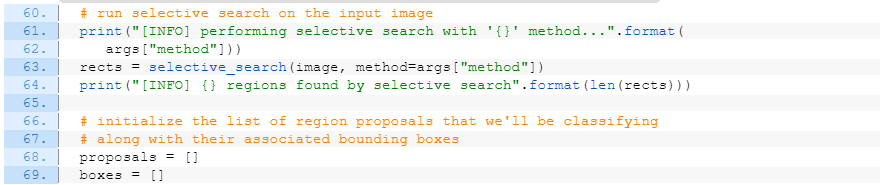
결과물: object region proposals가 담겨진 리스트 rects
다음 과정을 위해 두 개 빈 리스트(proposals, boxes) 생성
- proposals: 충분히 크기가 큰, 전처리가 된 ROI 이미지가 담길 예정, ResNet 분류기의 입력으로 활용
- boxes: proposals에 해당하는 박스의 좌표 담길 예정

전체 이미지의 10퍼센트 크기도 안 되는 것은 솎아내고, 전처리 실시(BGR2RGB, resize), 리스트 어펜드
분류기 모델에 넣고 돌리기

labelFilters와 --conf를 바탕으로 솎아내기.
labels 딕셔너리에는 key로 클래스 : value로 bounding boxes + probabilities를 가짐.
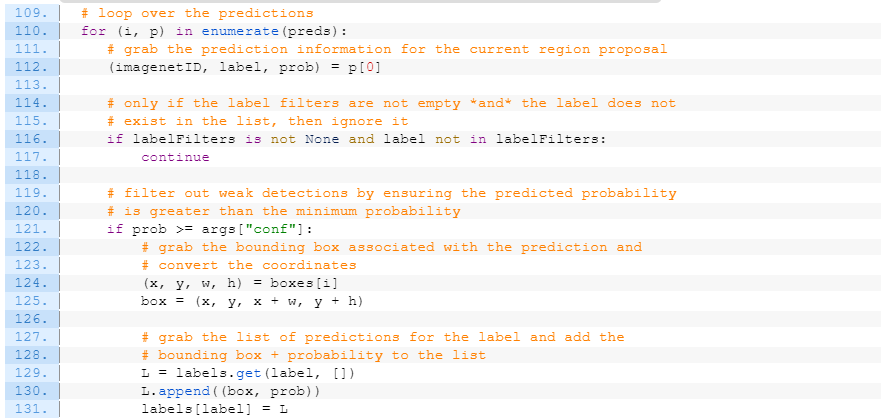
NMS 적용 전:
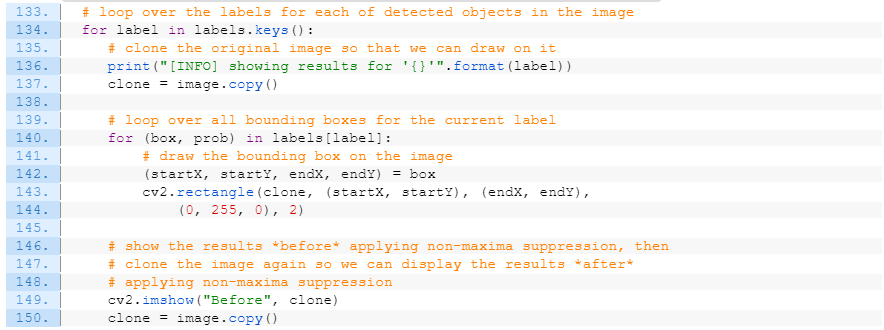
NMS 적용 후:

사용법:
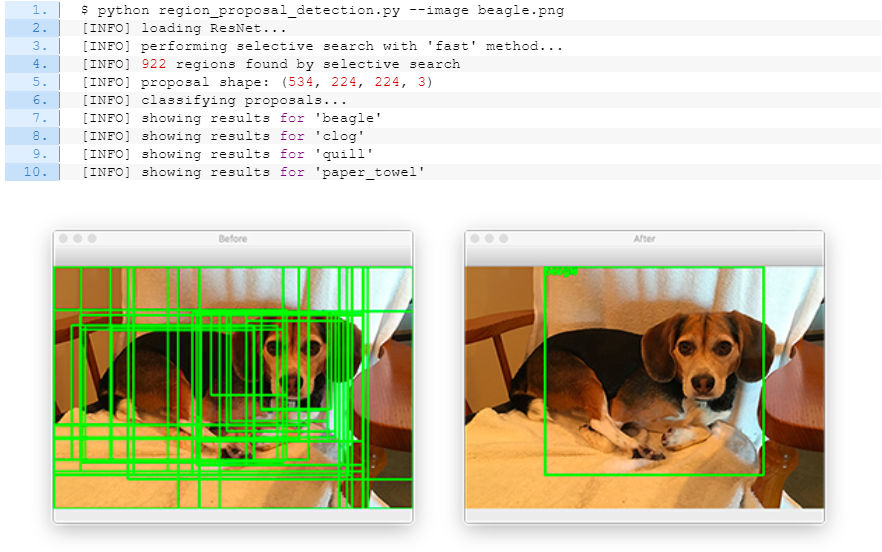
코드 정리:
# import the necessary packages
from tensorflow.keras.applications import ResNet50
from tensorflow.keras.applications.resnet50 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.applications import imagenet_utils
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from imutils.object_detection import non_max_suppression
import numpy as np
import argparse
import cv2
def selective_search(image, method="fast"):
# initialize OpenCV's selective search implementation and set the
# input image
ss = cv2.ximgproc.segmentation.createSelectiveSearchSegmentation()
ss.setBaseImage(image)
# check to see if we are using the *fast* but *less accurate* version
# of selective search
if method == "fast":
ss.switchToSelectiveSearchFast()
# otherwise we are using the *slower* but *more accurate* version
else:
ss.switchToSelectiveSearchQuality()
# run selective search on the input image
rects = ss.process()
# return the region proposal bounding boxes
return rects
# construct the argument parser and parse the arguments
ap = argparse.ArgumentParser()
ap.add_argument("-i", "--image", required=True,
help="path to the input image")
ap.add_argument("-m", "--method", type=str, default="fast",
choices=["fast", "quality"],
help="selective search method")
ap.add_argument("-c", "--conf", type=float, default=0.9,
help="minimum probability to consider a classification/detection")
ap.add_argument("-f", "--filter", type=str, default=None,
help="comma separated list of ImageNet labels to filter on")
args = vars(ap.parse_args())
# grab the label filters command line argument
labelFilters = args["filter"]
# if the label filter is not empty, break it into a list
if labelFilters is not None:
labelFilters = labelFilters.lower().split(",")
# load ResNet from disk (with weights pre-trained on ImageNet)
print("[INFO] loading ResNet...")
model = ResNet50(weights="imagenet")
# load the input image from disk and grab its dimensions
image = cv2.imread(args["image"])
(H, W) = image.shape[:2]
# run selective search on the input image
print("[INFO] performing selective search with '{}' method...".format(
args["method"]))
rects = selective_search(image, method=args["method"])
print("[INFO] {} regions found by selective search".format(len(rects)))
# initialize the list of region proposals that we'll be classifying
# along with their associated bounding boxes
proposals = []
boxes = []
# loop over the region proposal bounding box coordinates generated by
# running selective search
for (x, y, w, h) in rects:
# if the width or height of the region is less than 10% of the
# image width or height, ignore it (i.e., filter out small
# objects that are likely false-positives)
if w / float(W) < 0.1 or h / float(H) < 0.1:
continue
# extract the region from the input image, convert it from BGR to
# RGB channel ordering, and then resize it to 224x224 (the input
# dimensions required by our pre-trained CNN)
roi = image[y:y + h, x:x + w]
roi = cv2.cvtColor(roi, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
roi = cv2.resize(roi, (224, 224))
# further preprocess by the ROI
roi = img_to_array(roi)
roi = preprocess_input(roi)
# update our proposals and bounding boxes lists
proposals.append(roi)
boxes.append((x, y, w, h))
# convert the proposals list into NumPy array and show its dimensions
proposals = np.array(proposals)
print("[INFO] proposal shape: {}".format(proposals.shape))
# classify each of the proposal ROIs using ResNet and then decode the
# predictions
print("[INFO] classifying proposals...")
preds = model.predict(proposals)
preds = imagenet_utils.decode_predictions(preds, top=1)
# initialize a dictionary which maps class labels (keys) to any
# bounding box associated with that label (values)
labels = {}
# loop over the predictions
for (i, p) in enumerate(preds):
# grab the prediction information for the current region proposal
(imagenetID, label, prob) = p[0]
# only if the label filters are not empty *and* the label does not
# exist in the list, then ignore it
if labelFilters is not None and label not in labelFilters:
continue
# filter out weak detections by ensuring the predicted probability
# is greater than the minimum probability
if prob >= args["conf"]:
# grab the bounding box associated with the prediction and
# convert the coordinates
(x, y, w, h) = boxes[i]
box = (x, y, x + w, y + h)
# grab the list of predictions for the label and add the
# bounding box + probability to the list
L = labels.get(label, [])
L.append((box, prob))
labels[label] = L
# loop over the labels for each of detected objects in the image
for label in labels.keys():
# clone the original image so that we can draw on it
print("[INFO] showing results for '{}'".format(label))
clone = image.copy()
# loop over all bounding boxes for the current label
for (box, prob) in labels[label]:
# draw the bounding box on the image
(startX, startY, endX, endY) = box
cv2.rectangle(clone, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
# show the results *before* applying non-maxima suppression, then
# clone the image again so we can display the results *after*
# applying non-maxima suppression
cv2.imshow("Before", clone)
clone = image.copy()
# extract the bounding boxes and associated prediction
# probabilities, then apply non-maxima suppression
boxes = np.array([p[0] for p in labels[label]])
proba = np.array([p[1] for p in labels[label]])
boxes = non_max_suppression(boxes, proba)
# loop over all bounding boxes that were kept after applying
# non-maxima suppression
for (startX, startY, endX, endY) in boxes:
# draw the bounding box and label on the image
cv2.rectangle(clone, (startX, startY), (endX, endY),
(0, 255, 0), 2)
y = startY - 10 if startY - 10 > 10 else startY + 10
cv2.putText(clone, label, (startX, y),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.45, (0, 255, 0), 2)
# show the output after apply non-maxima suppression
cv2.imshow("After", clone)
cv2.waitKey(0)
#$ python region_proposal_detection.py --image beagle.png'Coding > Image' 카테고리의 다른 글
| NMS (Non-Maximum Suppression) (0) | 2021.04.14 |
|---|---|
| [4] RCNN Object Detection (0) | 2021.04.12 |
| [2] Selective Search (0) | 2021.04.12 |
| [1] CNN Image Classifier to Object Detector (0) | 2021.04.12 |
| matplot RGB vs opencv BGR vs caffe images (0) | 2021.04.09 |




